Sustainable construction materials for green buildings prioritize environmental responsibility, energy efficiency, and resource conservation, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient environment.
CopenHill represents a unique kind of waste-to-energy plant, featuring a ski slope, hiking trail, and climbing wall. It embodies the concept of hedonistic sustainability while also supporting Copenhagen’s aim to become the world’s first carbon-neutral city by 2025. PHOTO: ArchDaily
Are you interested in creating a positive impact on the environment while building your dream home or undertaking a construction project? Let me introduce you to sustainable construction materials. These are materials responsibly sourced and produced with the aim of minimizing environmental impact and promoting long-term sustainability. These materials encompass a wide range of options, including renewable resources, recycled content, low-carbon alternatives, and materials with a reduced ecological footprint.
The importance of sustainable construction materials in green building construction lies in their ability to enhance energy efficiency, reduce waste, and lower carbon emissions. By prioritizing the use of sustainable construction materials, green buildings not only contribute to a more sustainable future but also inspire industry-wide shifts towards environmentally conscious practices.
One of the concepts related to sustainable construction materials is embodied energy. When it comes to sustainable construction materials, one of their key advantages is their ability to minimize embodied energy. These materials are often sourced locally or regionally, reducing the energy required for transportation.
What is Embodied Energy?
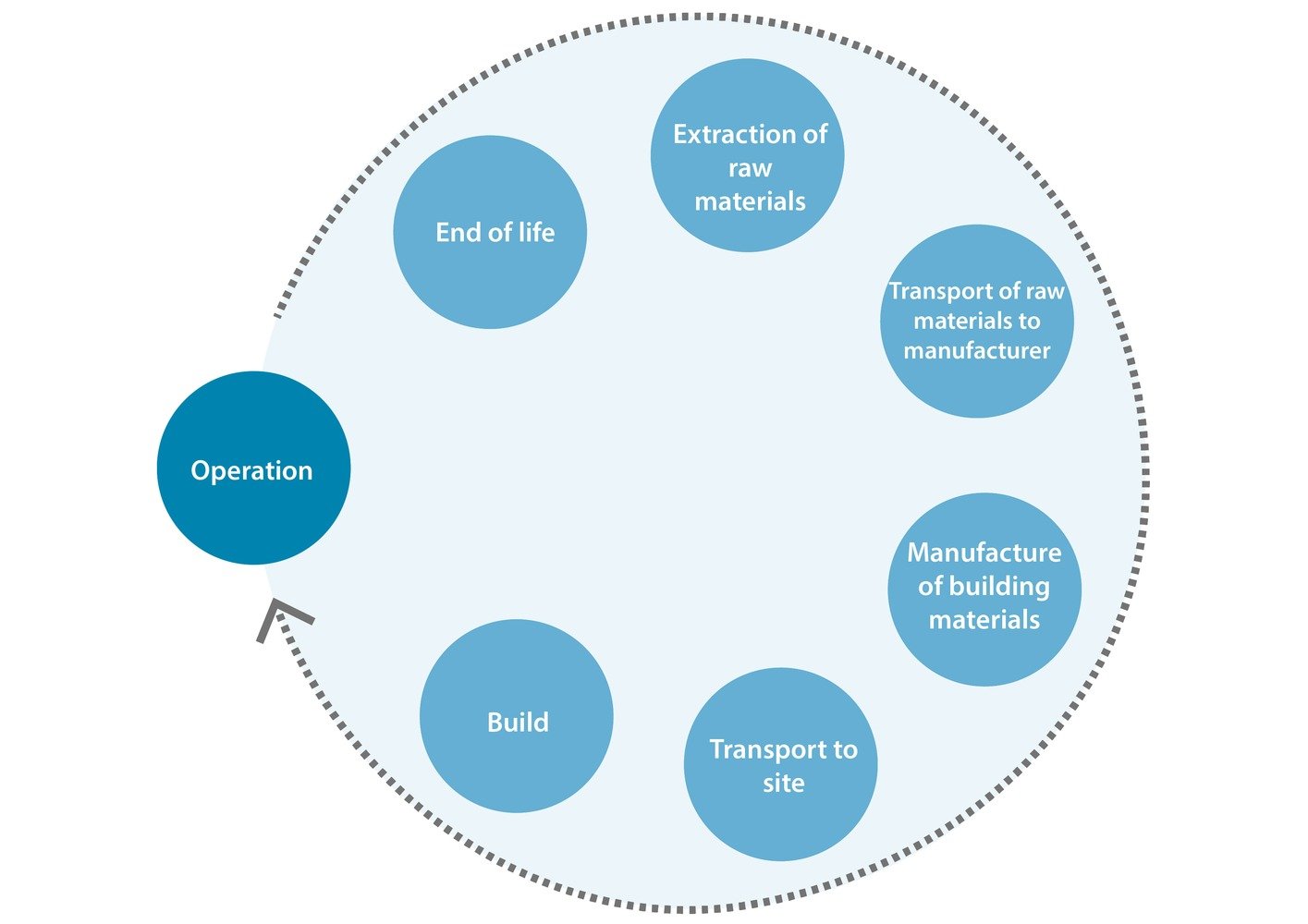
One crucial aspect to consider in the products we use in construction is embodied energy. According to EnergyEducation, embodied energy refers to the total energy consumed throughout a product’s life cycle, from extraction to disposal.
Embodied energy encompasses the energy required for various stages of a product’s life cycle. This includes the energy needed for raw material extraction, transportation, processing, manufacturing, distribution, and disposal, as per ArchDaily. It takes into account both direct energy (such as fuel and electricity used during manufacturing) and indirect energy (energy used for material production and equipment manufacturing).
PHOTO: ArchDaily
Sustainable construction materials, such as recycled materials, timber, natural materials, and high-performance concrete alternatives, play a vital role in reducing embodied energy. By repurposing materials, sourcing responsibly, and utilizing renewable resources, these materials significantly decrease the energy consumed throughout their life cycle. Additionally, materials like earth and natural materials, insulation, and green roofs have lower embodied energy.
Embodied energy is a crucial consideration in sustainability assessments. By quantifying the energy consumed throughout a product’s life cycle, we can have a comprehensive understanding of its environmental impact beyond just its usage phase. This information aids in making informed decisions about resource use, energy efficiency, and carbon emissions. By selecting products with lower embodied energy, individuals, architects, designers, and policymakers can contribute to reducing the carbon footprint and promoting sustainable practices.
Benefits of Sustainable Construction Materials
Sustainable construction materials offer numerous benefits that extend beyond environmental considerations. Firstly, sustainable construction materials prioritize environmental stewardship by reducing the demand for non-renewable resources and minimizing waste generation. These materials are often sourced responsibly, incorporating recycled content, renewable resources, or materials with low carbon footprints. Examples of this recycled materials, timber, natural materials, and high-performance concrete alternatives
Secondly, energy-efficient sustainable construction materials are designed to minimize energy consumption during the life cycle of a building, according to Nnamdi Ezimako. By improving energy efficiency, sustainable materials lower operational costs, decrease reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
Lastly, sustainable construction materials are known for their durability and longevity. Examples of this are earth and natural materials. They are designed to withstand harsh conditions, resist wear and tear, and have longer lifespans compared to conventional materials. This reduces the need for frequent replacements, which not only saves costs but also minimizes waste generation and the associated environmental impact.
Renewable and Recycled Materials
Renewable materials are derived from natural resources that can be replenished over time, as per Sustainable Build. Examples include timber from sustainably managed forests, bamboo, cork, and bio-based polymers. By utilizing renewable materials, we reduce our dependence on non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels and minerals. These materials offer numerous benefits, including low carbon emissions during production, improved energy efficiency, and reduced environmental impact.
Recycled materials are obtained by reprocessing and repurposing waste or discarded materials, giving them a new life cycle, according to Sustainable Build. Common examples include recycled concrete, recycled plastics, recycled metals, and reclaimed wood. By incorporating recycled materials, we divert waste from landfills, conserve energy that would be required for extracting and processing virgin materials, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with production.
Renewable and recycled materials find extensive use in the construction industry. Renewable materials offer sustainable alternatives to traditional building materials. Meanwhile, recycled materials reduce the environmental impact of construction while maintaining structural integrity and aesthetics.
Why We Should Use Sustainable Construction Material
Using sustainable construction materials is crucial for minimizing environmental impact, improving energy efficiency, and advancing circular economy principles. By prioritizing materials with low embodied energy, renewable resources, and recycled content, we can mitigate the depletion of finite resources, reduce carbon emissions, and promote the preservation of ecosystems.
Sustainable materials also contribute to energy-efficient buildings, healthier indoor environments, and long-term cost savings. Additionally, utilizing sustainable materials is a fundamental step toward constructing environmentally responsible and resilient green buildings.
Sources
-
Active Sustainability. (n.d.). Sustainable Building Material. Retrieved from https://www.activesustainability.com/construction-and-urban-development/sustainable-building-materials/?_adin=0744901958
-
Energy Education. (n.d.). Embodied Energy. Retrieved from https://energyeducation.ca/encyclopedia/Embodied_energy
-
Arch Daily. (2021). Embodied Energy in Building Materials: What it is and How to Calculate It. Retrieved from https://www.archdaily.com/931249/embodied-energy-in-building-materials-what-it-is-and-how-to-calculate-it
-
Nnamdi Ezimako. (2023). The Advantages of Using Sustainable Building Materials. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/advantages-using-sustainable-building-materials-nnamdi-ezimako#:~:text=Sustainable%20building%20materials%20reduce%20heat,of%20waste%20created%20during%20construction.
-
EHS Insight. (2020). The Benefits of Using Sustainable Building Materials. Retrieved from https://www.ehsinsight.com/blog/the-benefits-of-using-sustainable-building-materials
-
Smart Cities Dive. (2017). Understanding Recyclable and Renewable Materials for Sustainable Living. Retrieved from https://www.smartcitiesdive.com/ex/sustainablecitiescollective/understanding-recyclable-and-renewable-materials-sustainable-living/1329608/
-
Sustainable Build. (n.d.). Recycled or Renewable Resources? Retrieved from https://sustainablebuild.co.uk/recycled-or-renewable-resources/